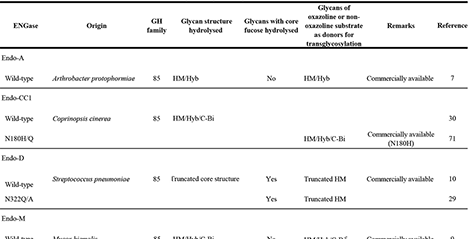
Endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase (ENGase) is an enzyme widely distributed among various organisms and known to hydrolyze N-glycans. Recent studies have demonstrated that strategic modification of its catalytic residues enables its conversion into a glycosynthase, thereby facilitating the chemoenzymatic remodeling of N-glycan structures.
In this series, we will discuss recent progress in glycoengineering-related ENGase research by leading experts in each field. ...and more
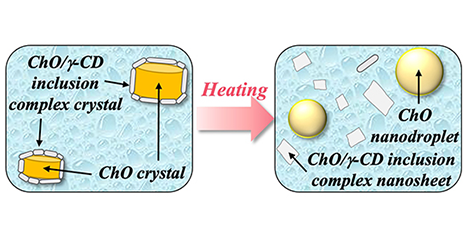
Pickering emulsions, in which cyclodextrin (CD) inclusion complex crystals precipitate at particle interfaces, have attracted considerable attention. In particular, Pickering emulsions composed of phytosterol ester (PSE) and γ-CD have been shown to be effective for masking capsaicin and controlling drug release. However, previous reports have focused on particles larger than 1 μm, and did not sufficiently investigate nanoparticle formation. In this study, we employed cholesteryl oleate (ChO), the main component of PSE, and optimized preparation conditions to successfully obtain ChO/γ-CD nanoparticles. These nanoparticles exhibited a unique core–shell structure, with a ChO crystal core surrounded by multiple nanosheets of ChO/γ-CD inclusion complex crystals forming the shell. Furthermore, the nanoparticles demonstrated dual-stimulus responsiveness, undergoing structural changes upon heating and exposure to bile components. Because they are prepared from inexpensive, safe, and easily handled raw materials, these nanoparticles hold promise as practical stimulus-responsive carriers for applications across diverse fields. ...and more